Why is Manufacturing Important?
May 28, 2022
American Made Really Does Matter
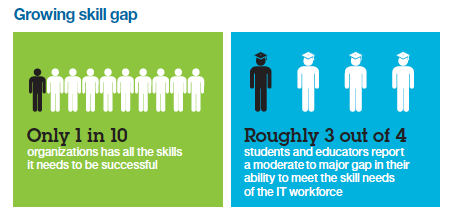
July 2, 2022In 2015, Deloitte predicted 2 million manufacturing jobs would remain unfilled by 2025 due to a gap in job skills. Publicly sounding an alarm many manufacturers already heard generated interest in creating marketing and educational programs to attract job candidates.
“Re-branding” to Mend the Manufacturing Skills Gap
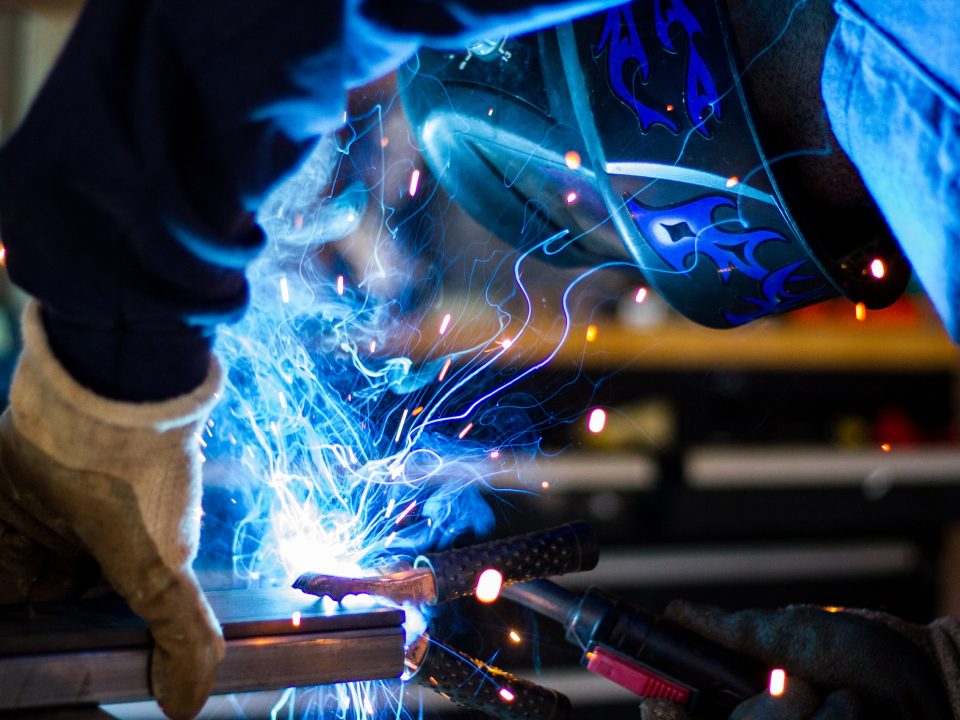
The manufacturing industry’s workforce has adapted throughout history as mechanization and automation evolved. Manufacturing would benefit from another re-branding. Today’s factory floors feature smart production that uses automation to enable communication between products and machines. This new manufacturing world has evolved from a ‘smokestack’ environment to one filled with clean air and high-tech opportunities.
Importantly, the shift toward automation isn’t prompting headcount reductions. A 2018 Manpower Group survey showed one in four companies plans to add jobs to support digital technology.
STEM programs (Science, Technology, Engineering and Math) have picked up momentum, but with a focus on medicine, engineering, and computer science – these skills are also needed across the new manufacturing landscape.
Providing Training to Mend the Manufacturing Skills Gap
An array of training and educational opportunities has emerged to draw younger workers into manufacturing.
- Aptitude Testing can measure skills and match employees with manufacturing roles they may not have pursued due to lack of experience. Demonstrating to applicants that they have the skills to succeed helps companies overcome misconceptions about manufacturing.
- Apprenticeships provide technical training in conjunction with more traditional college programs. These programs facilitate exposure to manufacturing industries and a guided ‘ramp-up’ to full time employment.
- Industry-led Curriculums where college coursework is developed with guidance (and equipment) from manufacturers can help students build the skill sets needed to succeed in industry.
- On-the-Job and Cross-Training keeps teams engaged and confident that they’re keeping pace with new technology and can take on multiple roles or switch roles with less downtime. For workers, continuous education allows them to develop skills to keep them employable long-term.
By showcasing the new manufacturing world and collaborating with educators on skills-training, manufacturers can bridge the skills gap and build careers.